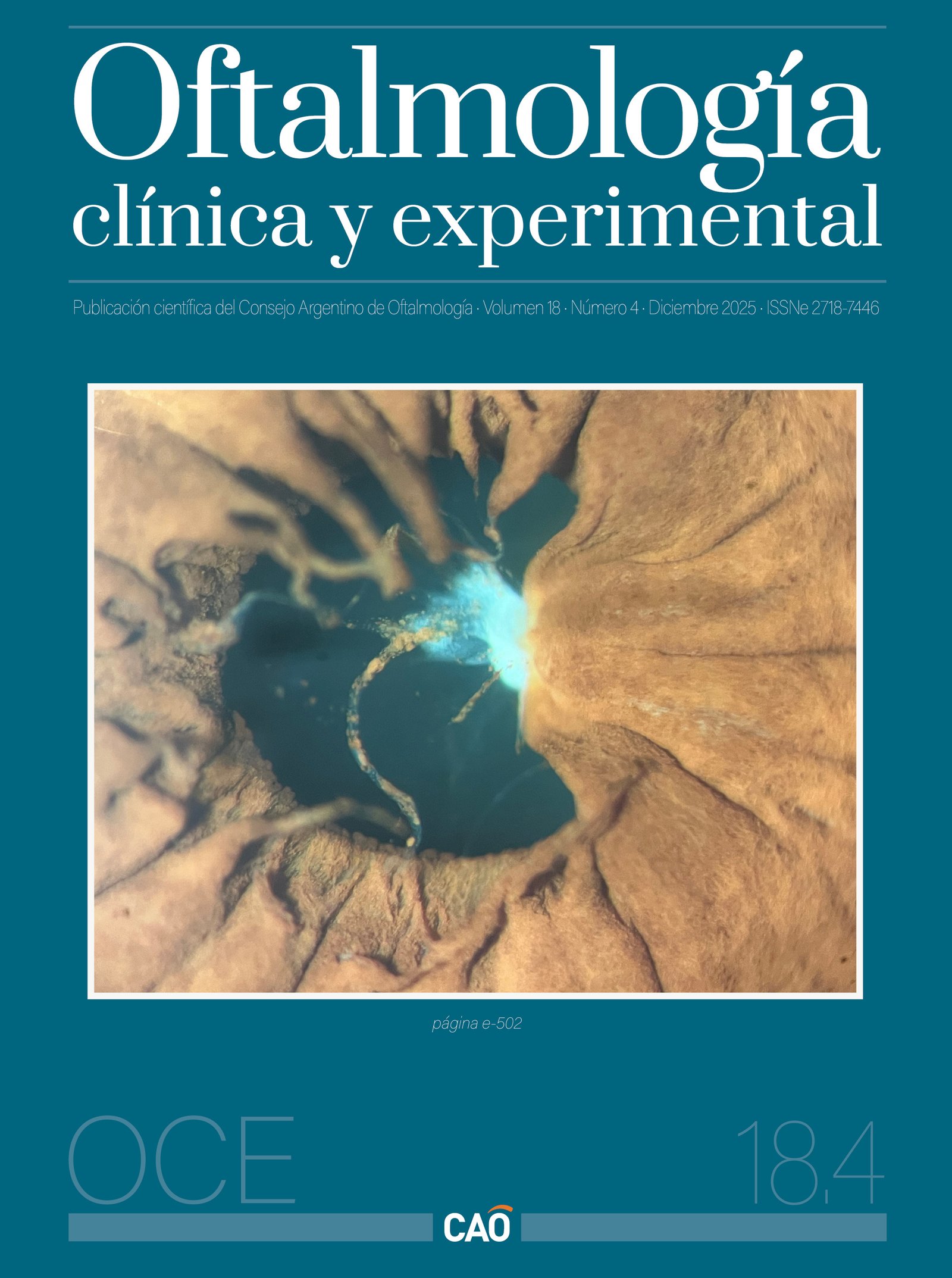
Acanthamoeba Sclerokeratitis
report of two clinical cases
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.70313/2718.7446.v18.n4.464Keywords:
scleritis, acanthamoeba, keratitis, sclerokeratitis, contact lens, abscessAbstract
Objective: To present two cases of Acanthamoeba keratitis associated with scleritis —an uncommon but severe manifestation— highlighting diagnostic challenges, therapeutic considerations, and their unfavorable clinical outcomes.
Case reports: We describe two adult patients with Acanthamoeba keratitis who progressed to nodular and subsequently necrotizing scleritis. Both received intensive anti-amoebic therapy (PHMB 0.02% + chlorhexidine 0.02%) and systemic immunosuppression due to scleral inflammation. Despite multidisciplinary management, both cases evolved poorly: the first patient developed corneal perforation and phthisis bulbi, requiring evisceration; the second patient experienced corneal perforation secondary to immune-mediated limbal failure, requiring urgent penetrating keratoplasty, and later died from systemic complications associated with immunosuppressive therapy.
Conclusion: The coexistence of Acanthamoeba keratitis and scleritis represents a severe and challenging entity with high risk of ocular loss and systemic complications. These cases underscore the importance of early diagnosis, aggressive treatment, and close follow-up, as well as prompt recognition of scleral involvement to optimize visual and systemic outcomes.
Downloads
References
1. de Lacerda AG, Lira M. Acanthamoeba keratitis: a review of biology, pathophysiology and epidemiology. Ophthalmic Physiol Opt 2021; 41(1): 116-135. doi: 10.1111/opo.12752.
2. Raghavan A, Rammohan R. Acanthamoeba keratitis: a review. Indian J Ophthalmol 2024; 72(4): 473-482. doi: 10.4103/IJO.IJO_2627_23.
3. Iovieno A, Gore DM, Carnt N, Dart JK. Acanthamoeba sclerokeratitis: epidemiology, clinical features, and treatment outcomes. Ophthalmology 2014; 121(12): 2340-2347. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2014.06.033.
4. Bataillie S, Van Ginderdeuren R, Van Calster J, Foets B, Delbeke H. How a devastating case of acanthamoeba sclerokeratitis ended up with serious systemic sequelae. Case Rep Ophthalmol 2020; 11(2): 348-355. doi: 10.1159/000508326.
5. Carnt N, Robaei D, Minassian DC, Dart JKG. Acanthamoeba keratitis in 194 patients: risk factors for bad outcomes and severe inflammatory complications. Br J Ophthalmol 2018; 102(10): 1431-1435. doi: 10.1136/bjophthalmol-2017-310806.
6. Dart JKG, Papa V, Rama P, Knutsson KA, Ahmad S, Hau S, Sanchez S, Franch A, Birattari F, Leon P, Fasolo A, Kominek EM, Jadczyk-Sorek K, Carley F, Hossain P, Minassian DC. The Orphan Drug for Acanthamoeba Keratitis (ODAK) Trial: PHMB 0.08% (polihexanide) and placebo versus PHMB 0.02% and propamidine 0.1. Ophthalmology 2024; 131(3): 277-287. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2023.09.031.
7. Carnt N, Robaei D, Watson SL, Minassian DC, Dart JK. The impact of topical corticosteroids used in conjunction with antiamoebic therapy on the outcome of Acanthamoeba keratitis. Ophthalmology 2016; 123(5): 984-990. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2016.01.020.
8. Roozbahani M, Hammersmith KM, Rapuano CJ, Nagra PK, Zhang Q. Therapeutic penetrating keratoplasty for acanthamoeba keratitis: a review of cases, complications and predictive factors. Int Ophthalmol 2019; 39(12): 2889-2896. doi: 10.1007/s10792-019-01137-1.
9. Di Zazzo A, Varacalli G, De Gregorio C, Coassin M, Bonini S. Therapeutic corneal transplantation in Acanthamoeba keratitis: penetrating versus lamellar keratoplasty. Cornea 2022; 41(3): 396-401. doi: 10.1097/ICO.0000000000002880.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Consejo Argentino de Oftalmología

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Con esta licencia no se permite un uso comercial de la obra original, ni la generación de obras derivadas. Las licencias Creative Commons permiten a los autores compartir y liberar sus obras en forma legal y segura.